Factors Influencing Cost and Stock Price
Cost stock price – A company’s stock price is intricately linked to its cost structure. Understanding this relationship is crucial for investors and businesses alike. Profitability, a key driver of stock valuation, is directly impacted by the efficiency of a company’s operations and its ability to manage costs effectively. This section will explore the various factors influencing both cost and stock price, examining their complex interplay.
The Relationship Between Production Costs and Stock Price
A company’s production costs directly influence its profitability. Higher costs, all else being equal, lead to lower profits, which in turn can negatively affect investor sentiment and subsequently depress the stock price. Conversely, efficient cost management and lower production costs contribute to higher profits and a more attractive stock valuation.
The Impact of Increased Raw Material Costs on Stock Prices
Fluctuations in raw material prices can significantly impact a company’s profitability and its stock price. For example, a surge in oil prices can severely affect the airline industry, increasing fuel costs and reducing profit margins. This, in turn, can lead to a decline in the airline company’s stock price. Similarly, increased lumber costs can impact homebuilders, affecting their profitability and potentially leading to a decrease in their stock valuation.
The Impact of Labor Costs on Profitability and Stock Valuation
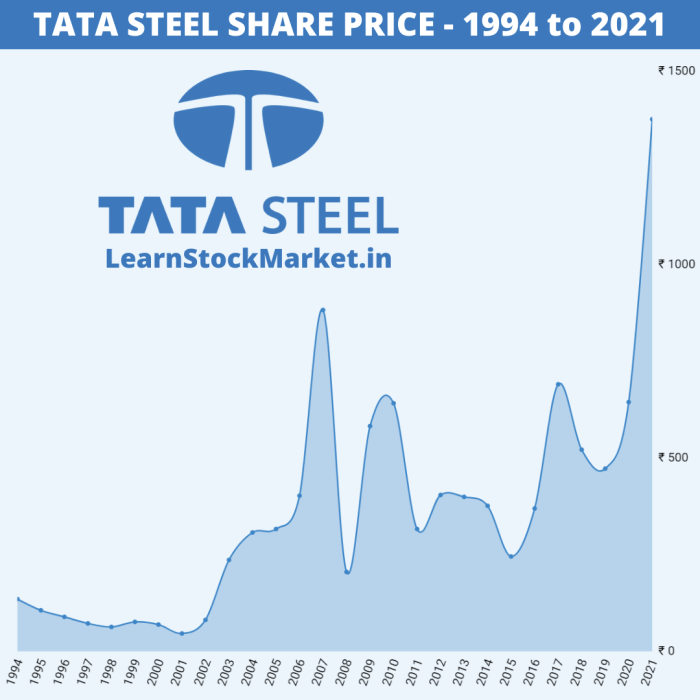
Source: learnstockmarket.in
Labor costs are a significant component of production expenses for many companies. Increases in minimum wage, union negotiations, or the need for specialized skills can all drive up labor costs. This can squeeze profit margins and negatively impact stock prices if not offset by increased productivity or pricing power. For example, companies in labor-intensive industries like manufacturing or hospitality are particularly susceptible to these pressures.
Industries Where Cost Fluctuations Significantly Impact Stock Prices
Industries heavily reliant on commodities or subject to significant price volatility in their inputs are particularly vulnerable to cost fluctuations. The airline industry (fuel costs), agriculture (fertilizer and water costs), and manufacturing (raw materials and energy costs) are prime examples. Even slight shifts in input costs can dramatically affect their profitability and, consequently, their stock prices.
Comparative Cost Structures and Stock Performance
| Company | Raw Material Costs (%) | Labor Costs (%) | Operating Margin (%) | Year-to-Date Stock Performance (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Company A | 30 | 40 | 15 | +10 |
| Company B | 20 | 50 | 12 | +5 |
This hypothetical example illustrates how differences in cost structure (Company A has lower raw material costs, while Company B has lower labor costs) can impact profitability and subsequent stock performance. Note that many other factors beyond cost influence stock prices.
Cost Reduction Strategies and Their Stock Market Impact
Implementing effective cost-reduction strategies is crucial for enhancing profitability and positively influencing a company’s stock valuation. This section will delve into various strategies and their impact on the stock market.
Various Cost-Cutting Strategies
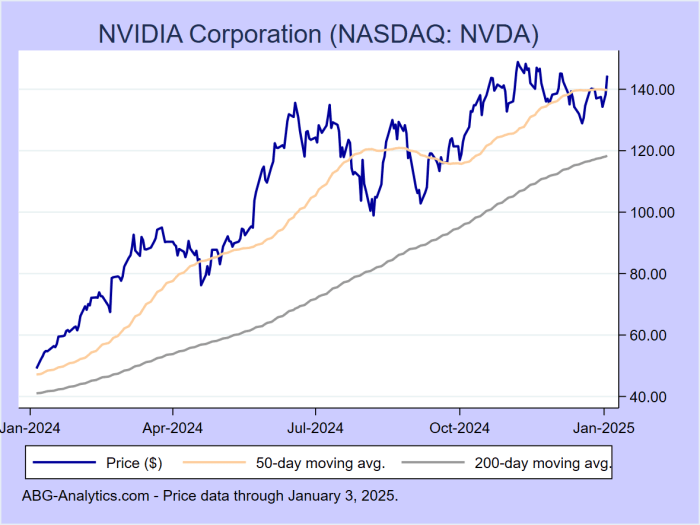
Source: abg-analytics.com
Companies employ a range of cost-cutting strategies, including streamlining operations, improving efficiency, negotiating better deals with suppliers, and investing in automation. These strategies can lead to significant savings and improve profitability, ultimately boosting the company’s stock price. Specific examples include lean manufacturing techniques, outsourcing non-core functions, and implementing enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems.
Efficient Supply Chain Management and Stock Price
Efficient supply chain management plays a vital role in reducing costs and improving profitability. Optimizing logistics, inventory management, and supplier relationships can significantly lower production costs. This enhanced efficiency translates to higher profit margins and a more positive perception among investors, potentially leading to an increase in the stock price.
Technological Advancements and Production Cost Reduction
Technological advancements offer significant opportunities for cost reduction. Automation, robotics, and advanced manufacturing techniques can enhance productivity, reduce labor costs, and minimize waste. These improvements in efficiency directly impact a company’s bottom line and can result in a higher stock valuation.
Short-Term and Long-Term Effects of Cost-Cutting Measures
Cost-cutting measures can have both short-term and long-term effects on stock prices. While some measures may yield immediate cost savings and a positive short-term stock price reaction, others, such as investments in new technology, might require initial investment before delivering long-term cost benefits and a sustained positive impact on the stock price.
Hypothetical Scenario: Successful Cost Reduction Initiative
Imagine a manufacturing company successfully implementing a new lean manufacturing process. This leads to a 10% reduction in production costs within six months. The resulting increase in profit margins boosts investor confidence, leading to increased demand for the company’s stock and a subsequent rise in its price. The market recognizes the company’s improved efficiency and future earnings potential.
Analyzing the Impact of Inflation on Cost and Stock Price
Inflation significantly impacts a company’s costs and, consequently, its stock price. Understanding its effects and the strategies used to mitigate them is essential for both investors and businesses.
Inflation’s Effect on Input Costs
Inflation increases the cost of inputs, such as raw materials, labor, and energy. This rise in input costs directly impacts a company’s production costs, squeezing profit margins and potentially leading to lower earnings and a decline in stock price. For example, rising energy prices can increase transportation costs for many businesses.
Hedging Against Inflation’s Impact
Companies employ various strategies to hedge against inflation’s impact. These include forward contracts for raw materials, long-term supply agreements, and diversification of suppliers. These measures help to mitigate the risk of increased input costs and protect profit margins.
Inflation Rates and Stock Market Volatility
High inflation rates often correlate with increased stock market volatility. Investors become uncertain about future earnings and the real value of their investments, leading to increased market fluctuations. This uncertainty can negatively affect stock prices, particularly for companies with limited pricing power.
Understanding a company’s cost structure is crucial for predicting its stock price performance. Factors like operational expenses and research and development directly impact profitability, which in turn influences investor sentiment. For instance, examining the current performance of paypal stock price reveals how these cost factors play out in the market. Ultimately, a thorough cost analysis provides a more informed perspective on a company’s long-term stock price trajectory.
Industries Vulnerable to Inflation’s Effects
Industries with high input costs and limited pricing power are particularly vulnerable to inflation’s effects. These include industries like agriculture, manufacturing, and transportation. Their profitability is directly tied to the cost of their inputs, making them susceptible to inflation-driven price increases.
Strategies to Mitigate Inflation’s Impact
- Implementing cost-cutting measures
- Raising prices strategically
- Improving efficiency to offset rising costs
- Investing in automation to reduce labor costs
- Hedging against inflation through contracts and diversification
Investor Sentiment and Cost-Stock Price Correlation
Investor sentiment plays a crucial role in determining how cost changes affect stock prices. Expectations about future costs significantly influence current stock valuations, often irrespective of the present reality.
Investor Expectations and Current Stock Prices
If investors anticipate future cost increases, they may react negatively even before these increases materialize. This anticipatory behavior can lead to a decline in stock prices, even if the company’s current profitability remains unaffected. This is because investors are forward-looking and price in their expectations of future performance.
Market Speculation and Stock Performance
Market speculation regarding cost increases can amplify their impact on stock prices. Rumors or news reports about potential cost hikes can trigger a sell-off, even if the actual cost increase is less significant than initially feared. This highlights the importance of accurate and timely communication from companies to manage investor expectations.
Analyst Reports and Investor Perceptions
Analyst reports and financial news play a significant role in shaping investor perceptions of the cost-stock price relationship. Analysts’ assessments of a company’s ability to manage rising costs influence investor sentiment and trading decisions. Positive assessments can support stock prices, while negative ones can lead to declines.
Sudden Cost Increases and Investor Confidence
A sudden, unexpected increase in production costs can significantly impact investor confidence. This can trigger a sell-off as investors reassess the company’s profitability and future earnings potential. The magnitude of the price drop depends on the severity of the cost increase and the company’s ability to mitigate its impact.
Visual Impact of Negative Cost News on Stock Price
Imagine a stock trading steadily around $50 for several weeks. Then, news breaks about a significant, unexpected increase in raw material costs for the company. The stock price immediately drops to $45, reflecting investor concern. Over the following days, the price might fluctuate but remains below the pre-news level as investors digest the implications of the higher costs.
If the company demonstrates effective cost management strategies, the price might gradually recover; otherwise, it could continue to decline.
The Role of Accounting Practices in Reporting Costs and Stock Valuation
Accounting practices significantly influence how production costs are reported and, subsequently, how a company’s stock is valued. Different methods can lead to varying reported profits and potentially affect investor perceptions.
Different Accounting Methods for Reporting Production Costs, Cost stock price
Various accounting methods exist for reporting production costs, including absorption costing and variable costing. Absorption costing allocates all manufacturing costs, both fixed and variable, to the products produced. Variable costing, on the other hand, only allocates variable manufacturing costs to products. The choice of method can significantly impact reported profits and, therefore, stock valuation.
Impact of Depreciation Methods on Reported Profits
The choice of depreciation method also influences reported profits and stock valuation. Accelerated depreciation methods, such as double-declining balance, result in higher depreciation expense in the early years of an asset’s life, leading to lower reported profits in those years. Straight-line depreciation spreads the expense evenly over the asset’s life, resulting in more consistent reported profits.
Potential Biases in Cost Reporting
Potential biases in cost reporting can influence stock prices. For instance, aggressive accounting practices might understate costs in the short term to boost reported profits, potentially attracting investors. However, this can lead to problems later on if the understated costs eventually need to be recognized.
Conservative versus Aggressive Accounting Practices
Conservative accounting practices tend to understate assets and overstate liabilities, resulting in lower reported profits. Aggressive accounting practices do the opposite. While aggressive accounting might boost short-term stock prices, conservative accounting offers greater transparency and long-term stability, potentially leading to greater investor confidence over time.
Different Accounting Methods and Reported Profits
| Accounting Method | Year 1 Profit | Year 2 Profit | Year 3 Profit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Absorption Costing | $100,000 | $120,000 | $110,000 |
| Variable Costing | $90,000 | $130,000 | $100,000 |
This hypothetical example illustrates how different accounting methods can lead to varying reported profits over time, potentially affecting investor perceptions and stock valuation.
Popular Questions: Cost Stock Price
How does currency fluctuation affect cost and stock price?
Currency fluctuations impact import/export costs, affecting profitability and stock price, particularly for companies with significant international operations. A stronger domestic currency lowers import costs, while a weaker currency increases export revenue but raises import costs.
What is the role of regulation in influencing cost and stock price?
Government regulations, such as environmental or labor laws, can increase production costs, impacting profitability and stock prices. Companies may need to invest in compliance measures, leading to higher expenses.
Can a company’s brand reputation affect its cost and stock price?
A strong brand reputation can command premium pricing, lowering cost pressures. Conversely, negative publicity can damage brand value, potentially requiring costlier remedial strategies and impacting stock prices negatively.